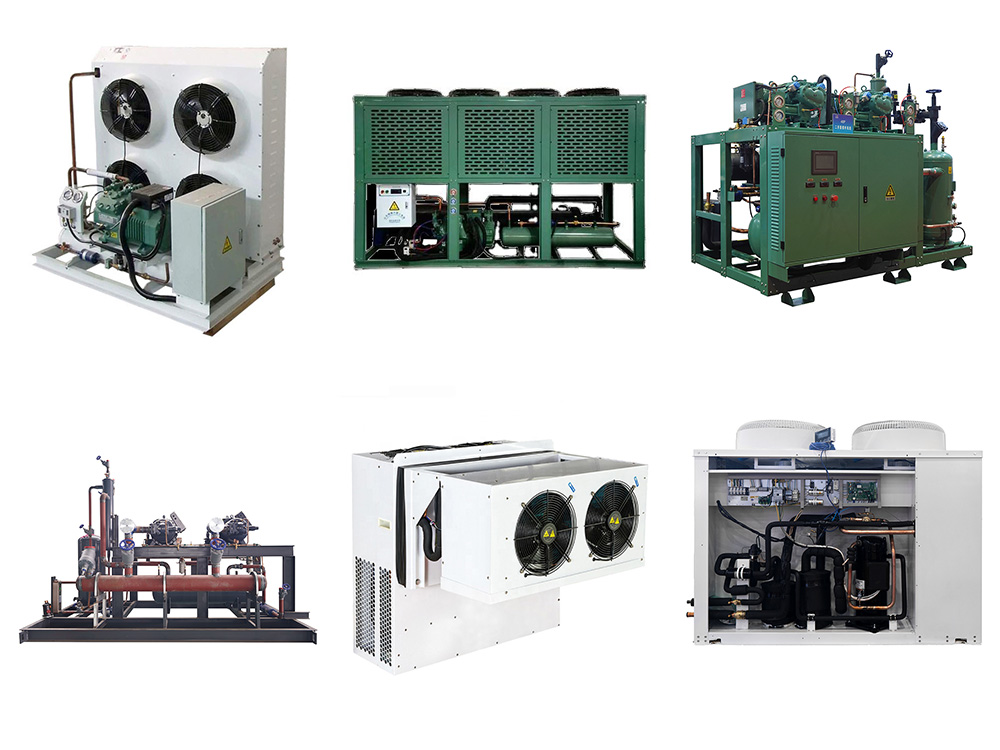
A refrigeration unit is a combination of equipment for creating a low-temperature environment via a refrigeration cycle to transfer heat.

I. Basic Principles
II. Main Components
III. Classification
IV. Application Scenarios

I. Basic Principles
- Vapor-compression Refrigeration: Comprising a compressor, condenser, throttling device and evaporator. The refrigerant in the evaporator absorbs heat from the cooled object and vaporizes. The compressor then compresses the vaporized refrigerant into a high-temperature, high-pressure gas. This gas enters the condenser to release heat and condense into a liquid. After passing through the throttling device for pressure reduction, it returns to the evaporator to start a new cycle.
- Absorption Refrigeration: Utilizes a binary solution (e.g., lithium bromide - water). The generator heats the solution, vaporizing the low-boiling-point component. The refrigerant vapor condenses in the condenser, passes through a throttle, and vaporizes in the evaporator to produce a refrigeration effect. The concentrated solution in the absorber absorbs the refrigerant vapor and returns to the generator.
II. Main Components
- Compressor: The core of the unit, compressing refrigerant gas. Types include piston, screw and centrifugal compressors.
- Condenser: Condenses refrigerant gas. Can be air-cooled (using air convection, simple but with lower efficiency) or water-cooled (using water, more efficient but requiring a water system).
- Evaporator: Where refrigerant absorbs heat and vaporizes, such as shell-and-tube or fin-and-tube types.
- Throttling Device: Reduces refrigerant pressure, like expansion valves (with adjustable flow) or capillary tubes (simple but with limited flow adjustment).
III. Classification
- By Refrigeration Capacity: Small (a few to dozens of kilowatts), medium (dozens to hundreds of kilowatts) and large (hundreds of kilowatts to several megawatts).
- By Cooling Method: Air-cooled (easy to install) and water-cooled (high efficiency).
- By Application Field: Air-conditioning, industrial and cold storage refrigeration units.
IV. Application Scenarios
- Commercial: In supermarkets for food preservation and in malls for air-conditioning.
- Industrial: For cooling chemical reactions and drug storage.
- Transportation: In refrigerated trucks and containers for transporting perishable goods.