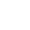
I. Building Structure
II. Refrigeration System
III. Electrical System
IV. Ventilation System
V. Auxiliary Equipment and Facilities
- Foundation: For small cold storages, a simple concrete foundation may suffice, while large ones, especially multi-story ones, demand a more elaborate foundation like pile foundation after geological survey. The foundation must be constructed precisely to prevent uneven settlement.
- Walls and Roof: The walls are typically made of sandwich insulation panels with metal outer layers and insulation like polyurethane foam in between. The roof, which can be sloping or flat, also requires insulation and waterproofing.
- Floor: It needs moisture-proof, insulation, and wear-resistant layers. A plastic film or coil is laid first for moisture prevention, followed by insulation, and then a wear-resistant surface like epoxy floor paint or wear-resistant concrete.
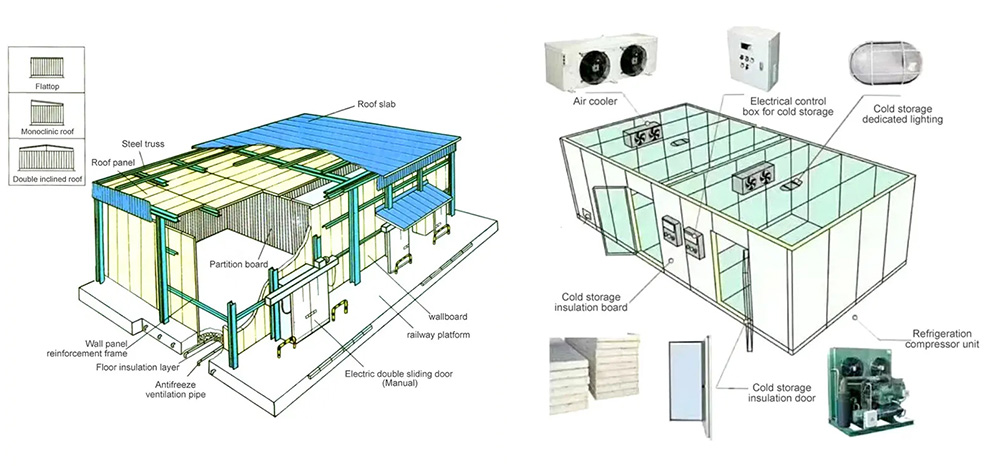
II. Refrigeration System
- Unit: Comprising a compressor (such as piston, screw, or scroll type), condenser (air-cooled or water-cooled), evaporator, and throttling device. The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant gas, the condenser cools it to liquid, the evaporator absorbs heat, and the throttling device controls refrigerant flow.
- Piping: Connects the unit components. Copper or seamless steel pipes are used, with valves and filters. The pipes must be well-sealed and insulated.
- Cooling System (if water-cooled): Consists of a cooling tower, pump, and piping. The tower cools the water for recycling, and the pump transports it to the condenser. The piping needs anti-corrosion treatment.
III. Electrical System
- Lighting: Uses moisture-proof and explosion-proof lamps, preferably LED, for sufficient illumination and energy efficiency.
- Power: Involves power distribution cabinets and boxes for supplying electricity to equipment. Wires and cables must be suitable for low temperatures and have protection features.
- Control: Monitors temperature and humidity via sensors and automatically adjusts the refrigeration unit. It also offers remote monitoring.
IV. Ventilation System
- Inside Storage: For goods with respiration, fans and ducts introduce fresh air and expel stale air. The ventilation volume depends on the goods and storage space.
- Machine Room: To dissipate heat from running equipment, mechanical ventilation with exhaust fans is used.
V. Auxiliary Equipment and Facilities
- Rack System: Metal racks with proper strength and low-temperature resistance are installed according to the goods type.
- Loading/Unloading and Transportation: A loading/unloading platform (fixed or adjustable) and transportation equipment like forklifts (with cold-resistant parts) are needed.
- Insulated Doors and Passageways: Insulated doors with good sealing and buffer passageways (air curtain or insulated) reduce heat transfer.